Walmart Store Sales Forecasting
This is a machine learning project available on Kaggle. The dataset provided has historical sales data for 45 Walmart stores located in different regions. Each store contains many departments and the objective is to project sales for each department in each store.
Data sets:
train.csv : This is the historical training data, which covers to 2010-02-05 to 2012-11-01.
test.csv : This file is identical to train.csv, except we have withheld the weekly sales. You must predict the sales for each triplet of store, department, and date in this file.
stores.csv :This file contains anonymized information about the 45 stores, indicating the type and size of store.
features.csv : This file contains additional data related to the store, department, and regional activity for the given dates.
Data Preparation:
The features dataset has a lot of missing values for the different markdown columns. I made an assumption here that the markdowns remain the same for a 2 week period in different years. So for the weeks where the markdown values are missing it is imputed by using the mean of the markdown across the years for which it is available.
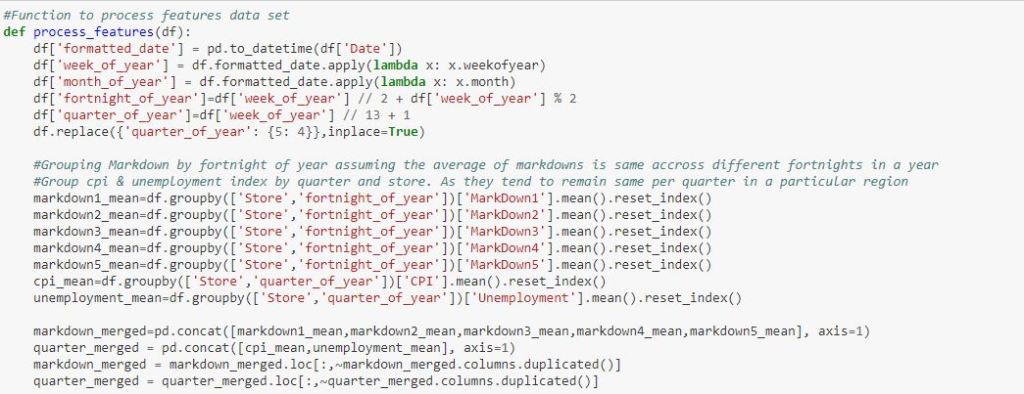
Feature Engineering:
We can create new features from the existing data elements like store type and holiday. We convert them to categorical numerical values. This is encapsulated in a function to apply the same logic to the holdout dataset.

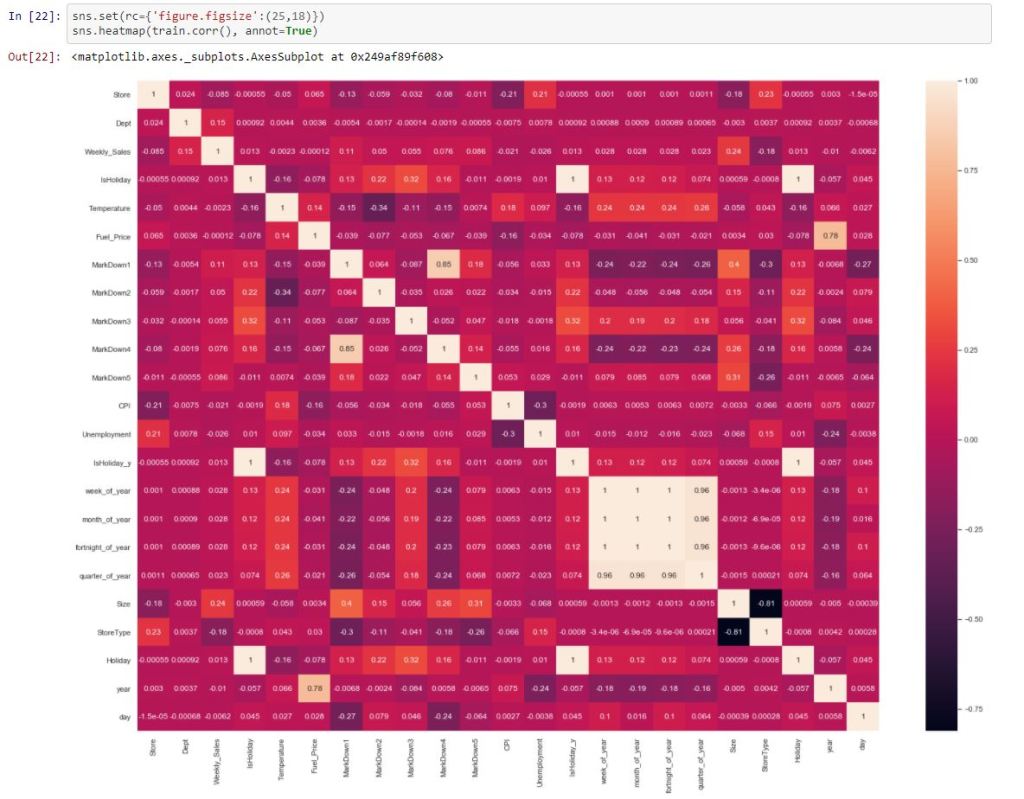
Feature Selection:
After looking at the correlation matrix and a couple of iterations of the model the following features were selected which provided the best results:
‘Store’,’Dept’,’week_of_year’,’month_of_year’,’year’,’day’,’Holiday’,’Temperature’,’Size’,’StoreType’
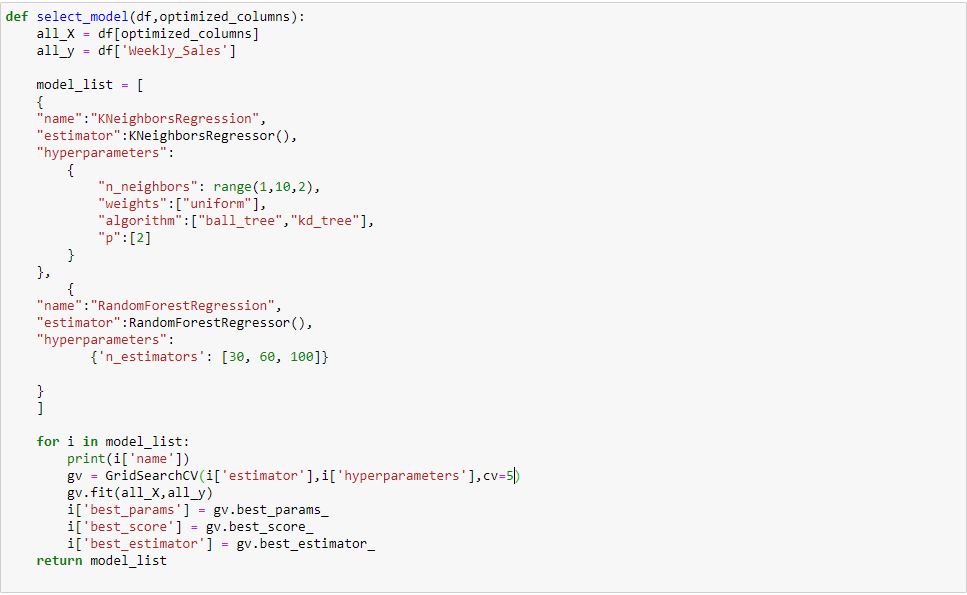
Model Tuning:
I created a function to determine the best model with the best hyperparameters. I use the GridSearchCV function that comes in Scikit-learns model selection package. This function can take some time as it has to try various permutations and combinations to determine the best hyperparameters to use.
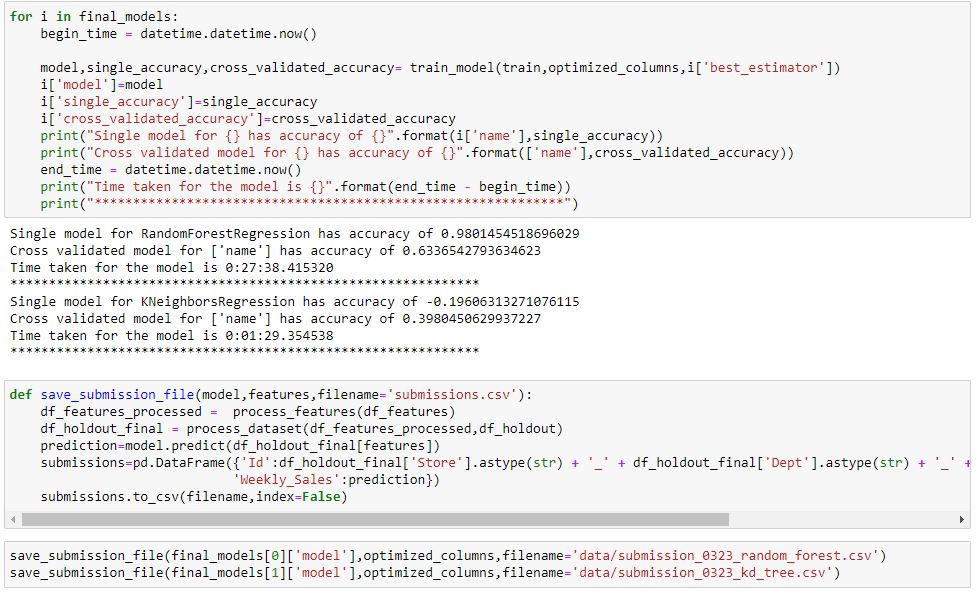
Final Model:
I use the train_test_split function available in Sklearn model selection package to split the training dataset and then the model is scored using the cross_val_score method.
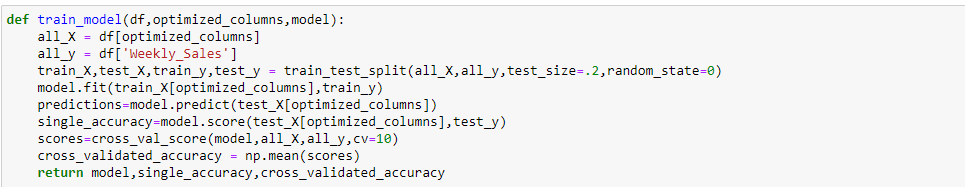
Since there are a couple of models with different hyperparameters I loop through the models to see which one has the best accuracy. The Random Forest model has the best accuracy and is used to generate the prediction.